Mental Health Career Paths: Counseling vs Therapy vs Psychology
Which mental health profession is right for me? Can I provide therapy as a counselor? Will I need a master’s degree to work as a school counselor? Do psychiatrists only work with severe mental illness? These may be questions that you have thought about when deciding to pursue rewarding work within many of the helping professions that work with all types of clients in many different settings.
Oftentimes, the terms of counseling and therapy are used interchangeably. Public perception of the two terms varies as one may be viewed as providing here and now services while the other delves deeper into root causes of behavior. However, both mental health terms relate to the services provided to individuals seeking guidance and assistance in addressing their social, emotional, and mental needs. In both, counselors or therapists are meeting with individuals to address their concerns on many different levels to include emotional, mental, and physical. There are different counseling theories that each mental health professional may integrate into their practice. As such, there could be many different titles and licensure/certifications for their practice.
Table of Contents
Explore what Counseling, Therapy and Psychology Careers have to offer. On this page you will be able to identify the disparities among these careers and dive deeper into the various fields that may interest you. Read more about the multiple career paths and prepare to take the next step in advancing into a profession.
Counseling Careers
Individuals who pursue a career in counseling often become one of the following: licensed professional, clinical mental health, school, rehabilitation, substance abuse, or pastoral counselor to name a few.
Therapy Careers
Therapy in the mental health field can be considered an overarching term that includes different types of approaches to meeting with clients. However, the term is not definitive of the level of competence a mental health professional will have.
Psychology Careers
Psychologists are trained to perform assessments, make diagnoses, and provide therapy to individuals & groups. The different types of concentrations determines the title of a psychologist to include population and locale of practice.
Social Work Careers
Social workers provide social services and resources to people and communities who need help coping with the problems impacting their lives. Clinical social workers diagnose and provide treatment for mental health issues.
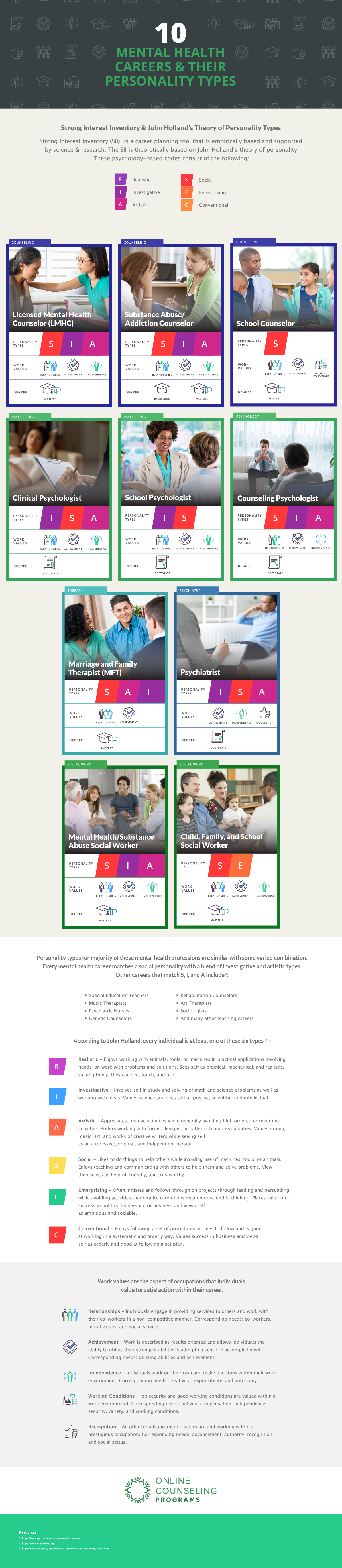
Counseling Careers
Licensed Mental Health Counselor (LMHC)
Mental health counselors provide client-centered therapy through the combination of psychotherapy with a problem-solving approach to address change and problem resolution. The American Mental Health Counselors Association (AMHCA) summarizes the services that are offered by LMHC’s to include assessment & diagnosis, psychotherapy, treatment planning, brief- and solution-focused therapy, alcohol and substance abuse treatment, psychoeducational and prevention programs, and crisis management.
Who do licensed mental health counselors work with?Licensed Mental Health Counselors also work with other mental health professionals in collaboration for the health and benefit of their clients.
How to Become a Licensed Mental Health CounselorSome counseling specialties, such as a mental health or professional counselor, require licensure before earning certification to work with a specific population. To become an LMHC, one must obtain a master’s degree in clinical mental health counseling and licensure.
Licensed Professional Counselor (LPC)
Become an LPC with one of our sponsored online psychology programs.
Professional counselors diagnose and treat mental and emotional disorders through psychoeducational techniques, prevention plans, consultation, and therapy.
Who do professional counselors work with?LPCs work with individuals, families, and groups to address mental, behavioral, and emotional problems and disorders. The Licensed Professional Counselors Board of Examiners summarizes that LPCs are licensed to provide Mental Health Counseling and Psychotherapy Services independently to the public. The counselor takes one the role of responsibility for knowledge, skill, and ethical consideration needed to assist individuals, groups, organizations, or the general public.
How to Become a Licensed Professional CounselorSimilar to LMHCs, licensed professional counselors (LPCs) must be licensed and obtain their master’s degree in counseling or a related field and licensure to practice. Supervised clinical work is typically required to get your license. Each state will have different licensing, certification and clinical experience requirements for how to become an LPC. Make sure to check with your state’s licensing board.
Sponsored Online Counseling Programs

Northwestern University
The Family Institute at Northwestern University
Master of Arts in Counseling
Earn a CACREP-accredited master’s in counseling online from top-9 ranked1 Northwestern University.
1U.S. News & World Report: 2022 Best National University Rankings
- CACREP Accredited
- Earn your MA in Counseling from Northwestern in as few as 18 months
- Accelerated full-time, traditional, or part-time tracks available

New York University
NYU Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development
Master of Arts in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness
Aspiring mental health counselors are prepared to pursue licensure with NYU Steinhardt’s MPCAC-accredited online counseling master’s. Students can earn their degree in as few as 21 mos. GRE not req.
- Prepare to become a mental health counselor
- Accredited by the MPCAC
- As few as 21 months to complete
- GRE not required
Substance Abuse/Addiction Counselor
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides an outline of typical substance abuse/addiction counselor activities. Substance abuse/addiction counselors evaluate a client’s mental and physical health to assess readiness for treatment.
Who do substance abuse counselors work with?Helping to define goals and subsequent treatment plans, substance abuse/addiction counselors work with clients to develop the skills and behaviors that are necessary for recovery from addiction or to modify their behavior. These counselors also educate families about addiction and the process of recovery.
How to Become a Substance Abuse CounselorFor some specialty certifications, various states will certify individuals who were addicts to provide peer counseling. Depending upon the locale and place of practice, substance abuse counselors may have a bachelor’s education, while others earn licensure after completing a recognized master’s degree program.
School Counselor
The ASCA examines in their role statement of school counselors that they engage in activities to promote equity and equal access to educational experiences for all students through leadership, advocacy, and collaboration to support a safe environment for learning.
Who does a school counselor work with?School counselors address the needs of all students through a culturally relevant lens while integrating intervention programs that are a part of the comprehensive school counseling program.
How to Become a School CounselorAll school counselors are required to obtain an advanced degree such as a master’s degree in school counseling. In some states, according to the American School Counselor Association (ASCA), you must have teaching experience before becoming certified in school counseling. Check their State Certifications page for more information.
School counseling and school social work have some similarities, like working with students to discover learning struggles and create solutions. However, there are some key differences between what a school counselor and school social worker does. The requirements to become a school counselor are also different than the requirements to become a school social worker. Each state has its own school counselor licensing requirements.
Sponsored Online School Counseling Programs

University of Denver
Morgridge College of Education Online
Master of Arts in School Counseling
Advocate for P-12 students and become an agent of change in your community. With no GRE required, earn your Master in School Counseling online in as few as 24 months from the University of Denver. Gain valuable skills through a CACREP accredited curriculum centered on social justice.
- No GRE required
- Live, online classes
- Complete in as few as 24 months
Therapy Careers
Licensed Therapist
Different Kinds of Therapists
There are many types of therapy careers, including:
- Psychotherapists
- Marriage and family therapists
- Applied behavioral analysis (ABA) therapists
- Recreational therapists
- Child therapists
- Cognitive behavioral therapists (CBTs)
How to Become a Licensed Therapist
To become a licensed therapist, you’ll need to complete educational, experience, exam and licensure requirements. Each state’s requirements may vary depending on the type of therapist role you want to pursue.
Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist (LMFT)
They treat issues that are common in those types of relationships. According to the American Association for Marriage and Family Therapy (AAMFT), LMFTs address depression, marital problems, anxiety, psychological concerns and child-parent problems. Therapy approaches for LMFTs involve a holistic, brief- and solution-focused therapy with therapeutic goals that are attainable. Comparing LMFT vs. mental health counselor (LPC) roles, LMFTs work specifically with married couples and families.
Who do MFTs work with?Marriage and family therapists address clinical concerns with individuals, couples and marriage session groups. MFTs discuss the role of the individual within marriage or family dynamics and how it might influence the presenting concern. MFTs assess, diagnose and treat mental health disorders. The difference between marriage and family therapists vs. psychiatrists is that psychiatrists can prescribe medication for mental disorders, while MFTs cannot.
How to Become an MFTTo become an MFT, individuals must pursue a master’s degree in psychology, marriage and family therapy, or a related mental health field and apply for licensure through their state board. Once you become an MFT, you may pursue certifications to specialize in a certain population or gain expertise in a type of marriage and family therapy method.
Board-Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA)
Education Requirements for BCBAs
Aspiring board-certified behavior analysts must obtain a master’s in applied behavior analysis or another relevant field. Application requirements vary by ABA master’s program but may include a resume, letters of recommendation and a personal statement.
What do BCBA therapists do?
BCBA therapists influence an individual’s behavior by using applied behavior analysis (ABA) therapy. ABA therapy focuses on improving specific behaviors, such as learning, socializing, communication and occupational competence.
Who do BCBA therapists work with?
BCBA therapists work with those who have mental health issues, developmental disabilities or special needs, like autism. They may work in environments such as schools, hospitals and nonprofits.
How to Become a BCBA
To become a behavior analyst, you’ll need to take and pass the BCBA exam. First, you must meet certain educational, experience and exam requirements.
Psychology Careers
There’s a wide variety of specialty careers in psychology you may pursue. Getting a master’s degree in psychology may be a good place to start to launch a career in psychology. Another option is a doctoral degree in psychology, which is typically a requirement to become a licensed psychologist.
Clinical Psychologist
Education Requirements for Clinical Psychologists
Clinical psychologists are required to have a doctoral degree in psychology, which can come in the form of a PsyD or PhD. While a master’s in clinical psychology is typically not required to apply for a psychology doctoral program, some doctoral programs require applicants to have a psychology master’s degree. After obtaining their doctorate, clinical psychologists are trained to provide individual and group therapy.
What do clinical psychologists do?
Providing mental and behavioral health services in both health and social care settings, clinical psychologists use scientific approaches to focus on prevention, health disparities, reduce psychological distresses, and to enhance psychological well-being.
Who do clinical psychologists work with?
The American Psychological Association (APA) describes the role of psychologists as including the following: assessment, diagnosis, collaboration with an interdisciplinary team, creating/monitoring programs of treatment, offering therapy, rehabilitation of clients into community, developing programs for behavioral and mental health services, consulting with other professionals and staff, and conducting evidence-based research.
A main difference between therapist vs. clinical psychologist roles is that clinical psychologists typically have a doctoral degree and may provide additional services such as consultation, training, education, supervision and clinical research.
How to Become a Clinical Psychologist
To become a psychologist, you’ll need education, an internship or postdoctoral program, and a psychologist license. Check requirements in the state where you want to work.
Behavioral Psychologist
Education Requirements for Behavioral Psychologists
Behavioral psychologists typically need to have a doctoral degree in psychology. Some choose to pursue a master’s in behavioral psychology to prepare.
What do behavioral psychologists do?
Behavioral psychologists help patients modify behavior. They use research-backed practice and techniques including therapy, education and monitoring.
Who do behavioral psychologists work with?
Behavioral psychologists work with a variety of patients, ranging from children to adults in environments like research centers, mental health clinics, and as expert witnesses in court cases. They might also work as a consultant with organizations.
School Psychologist
Education Requirements for School Psychologists
School psychologists also obtain their doctorate degree, make diagnoses, and provide therapy much like their clinical counterpart. School psychologists, however, work with parents, teachers, and school staff to address the developmental needs of students as well as the formation of individual education plans (IEP).
What do school psychologists do?
The National Association of School Psychologists (NASP) examines that school psychologists help schools to improve academic achievement, promote positive behavior and mental health, support diverse learners, create a safe and positive school climate, strengthen family-school partnerships, and to help improve school-wide assessment and accountability for student progress in academics and behavior.
Who do school psychologists work with?
Collaborating with other student support staff, like school counselors, psychologists in the school settings work to promote the overall behavioral and mental health of their students.
How are school psychologists different from school counselors? Learn more in our comparison guide: School Counselor vs. School Psychologist
Educational Psychologist
Education Requirements for Educational Psychologists
Like most psychologists, educational psychologists have a doctoral degree in psychology. There are doctorate in educational psychology degrees students might pursue that focus specifically on psychology in an educational setting. There are also master’s in educational psychology degrees available to prepare aspiring educational psychologists.
What do educational psychologists do?
Educational psychologists apply psychological principles and techniques to improve school and student outcomes. Educational psychologists focus on how to improve learning methods and the instructional process.
Who do educational psychologists work with?
Educational psychologists may work with students to treat learning problems. They may also consult school-based professionals to improve learning, teaching and administrative strategies.
Counseling Psychologist
Education Requirements for Counseling Psychologists
Working with all types of populations and organizations, to include businesses, counseling psychologists have earned their doctorate in their field. There are also master’s degrees in counseling psychology which, while they do not lead to psychology licensure, may lead to acquiring counseling licensure.
What do counseling psychologists do?
This profession also provides assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of severe psychological symptoms. The American Psychological Association (APA) further identifies counseling psychologists as engaging in individual, group, and family counseling and psychotherapy providing many services such as crisis intervention and trauma and disaster management while consulting with organizations and providing program evaluation and tracking client progress.
Who do counseling psychologists work with?
As general practice and health service providers, counseling psychologists address the emotional, social, work, school, and physical health concerns of individuals and focus on how people function both personally and within their relationships.
Health Psychologist
Education Requirements for Health Psychologists
Health psychologists typically need a doctoral degree in psychology. Psychology doctoral programs may require a master’s in psychology degree.
What do health psychologists do?
Health psychologists study how people handle illness. They work with patients to improve health and pain management and develop healthcare strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Who do health psychologists work with?
Health psychologists may work with patients in medical settings like hospitals, and with healthcare administrators and professionals like medical doctors.
How to Become a Health Psychologist
To become a health psychologist, there are educational, practice and licensure requirements. Each state will have its own licensure requirements.
Psychiatry Careers
For those who pursue a career in psychiatry, they receive medical training and education to become a doctor who can prescribe medication based upon the mental and physical assessment of any client.
Psychiatrist
What is psychiatry?
Psychiatry is a branch of medicine that is focused on mental health that include substance use disorders.
What do psychiatrists do?
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) reviews that psychiatrists are educated and trained on a medical route to focus on diagnosis, treatment, and prevention or mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders which include physical aspects of psychological concerns. Oftentimes, psychiatrists will prescribe medications in combination with the therapy that they offer.
Education Requirements for Psychiatrists
After completion of their doctorate program, psychiatrists complete over four years of residency within a hospital working with medical illnesses. The remaining three years are dedicated to mental health treatments.
Social Work Careers
Social workers can make diagnoses, provide individual and group therapies, and provide case management and advocacy on behalf of their clients.
Licensed Master Social Worker (LMSW)
What is the role of social workers?
Licensed master social workers work with people and communities in need of help. They research and refer clients to resources that improve their well-being. LMSWs may also respond to crisis situations, develop social work programs and advocate for disadvantaged communities.
Where do social workers work?
LMSWs work in a variety of settings, including nonprofits, government agencies, schools, hospitals, substance abuse facilities and community centers.
Education Requirements for Social Workers
Social worker licensure requires a master’s in social work from a school that is accredited by the Council on Social Work Education.
How to Become a Licensed Master Social Worker
To become a licensed social worker, a social worker must meet state licensure expectations. Typically these include education, field experience and exam requirements.
Licensed Clinical Social Worker (LCSW)
What is the role of clinical social workers?
Licensed clinical social workers help individuals, families, and groups increase their capacity in social functioning and advocate for conditions in society that support their communities. LCSW helps individuals address their own needs through psychosocial services and advocacy.
Where do clinical social workers work?
Social workers can be found in schools, hospitals, mental health clinics, senior centers, private practice, prisons, and in other agencies that address individual and family needs.
Education Requirements for Clinical Social Workers
Licensed clinical social workers are first educated through a recognized social work master’s degree program and then apply for licensure through their state board. The education requirements to become an LCSW are the same as the ones for an LMSW. However, the social work licensure requirements for an LCSW are different. When comparing social work vs. psychology careers, LCSW requirements will also differ.
How to Become a Licensed Clinical Social Worker
To become a licensed clinical social worker, you’ll have to meet education, experience, exam and licensure requirements set by the state board where you want to practice.
Ever wonder about the difference between counselors and social workers? Learn more in our comparison guide: Mental Health Counselor vs. Social Worker.
Although each discipline of mental health professions varies from one another, they all involve the advocacy and attention to the mental health needs and concerns of their clients – from all walks of life and in many different locales and places of practice. In determining which profession is right for you, take into consideration the importance of working with specific populations, the roles that you would like to play, and which setting you would like to practice in. There are many other specialties, certifications, endorsements, and licenses that are available to those seeking to become a mental health professional.
Last updated: September 2020
Sources: